Obesity in Dogs

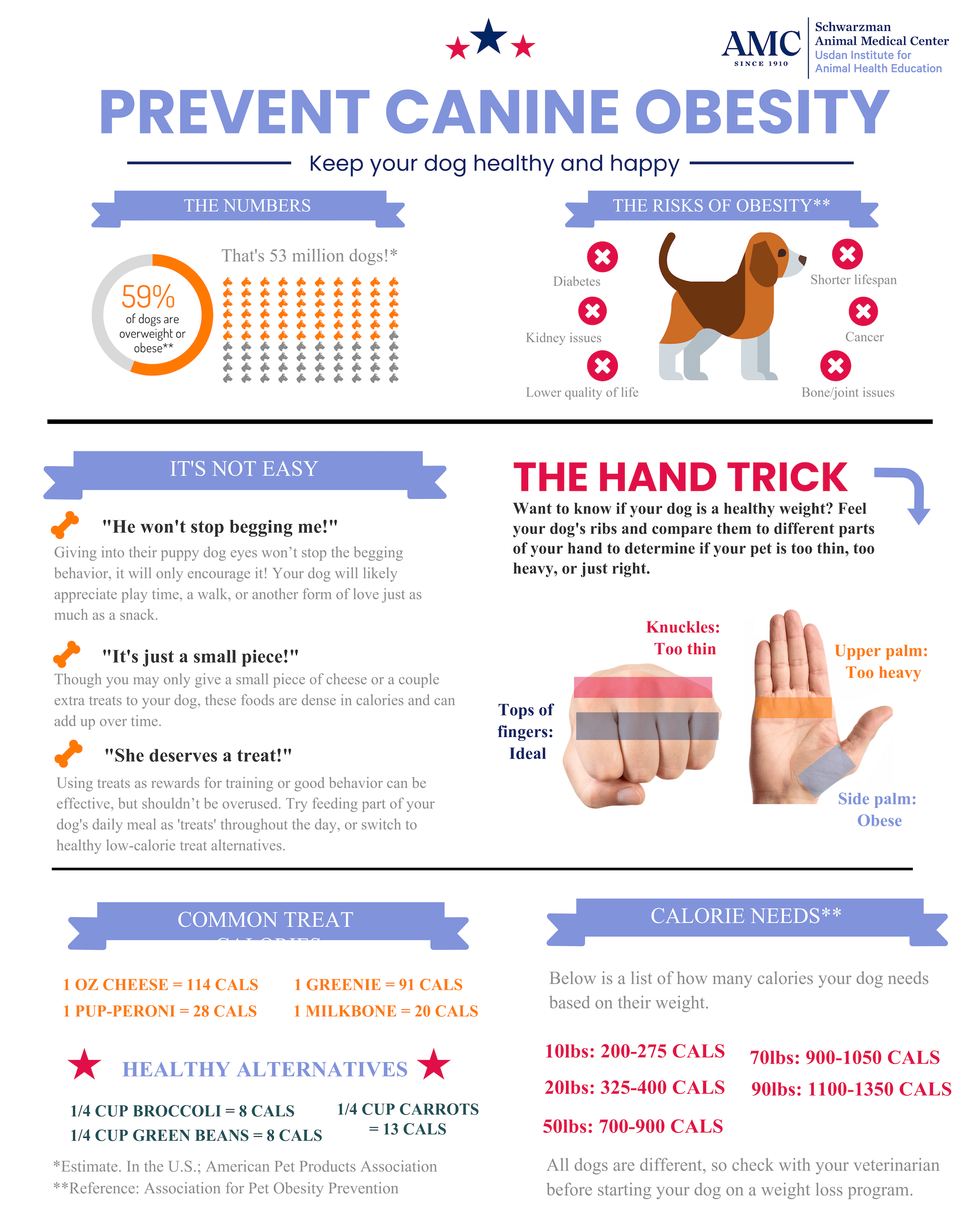
The Association for Pet Obesity Prevention estimates that 59% of dogs are overweight or obese. In animals, fat starts to accumulate around internal organs before it’s visible from the outside. That means by the time you notice your dog has gained weight, his health may already be negatively affected.
Being overweight or obese doesn’t just affect how your dog looks, it also increases his risk for many health problems including:
- Cancer
- Decreased lifespan
- Heart disease
- Kidney issues
- Type 2 Diabetes and insulin resistance
- Osteoarthritis
If your dog does become overweight or obese, talk with your veterinarian about ways to get your pup back to a healthy weight. This could include a change in diet or starting an exercise program. Your veterinarian can help you find a solution that works best for you and your dog.
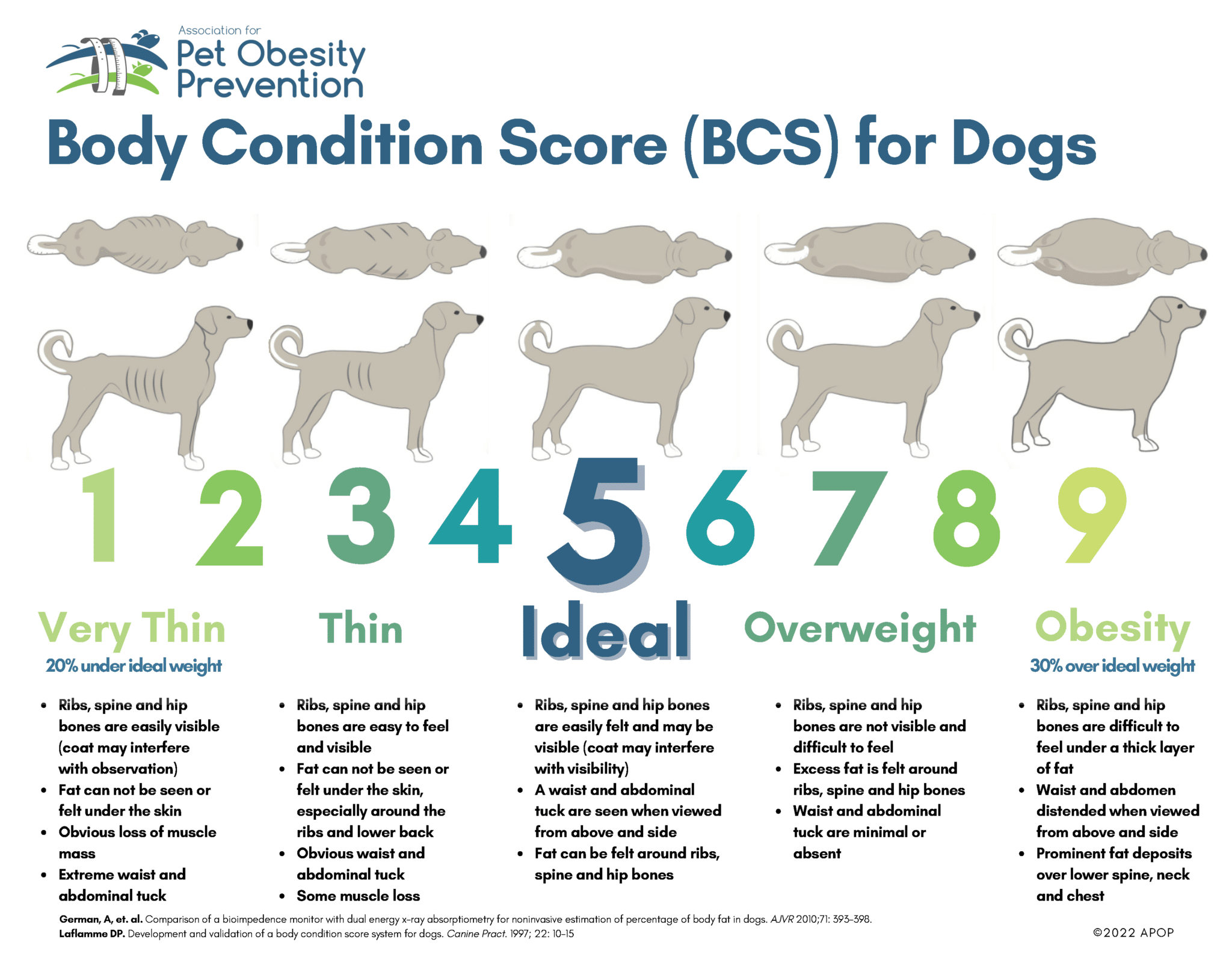
Body Condition Scoring (BCS) is a quantitative tool that is used to determine a dog’s body condition and fat accumulation. The scale ranges from 1 (very thin) to 9 (obese) with an ideal body score of 5. Changes in a pet’s weight can have many causes including dietary changes, feeding habits, physical activity, age, medication, as well as an underlying disease.
Make sure to discuss your pet’s ideal weight and nutritional needs with your veterinarian.